By all means, please help fix spelling, grammar, and organization problems. Thank you.
| Commonwealth of Cascadia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
|
Motto: English: "My Law, On The Land" Latin: Lex Mea In Terra | |||||
 Location of Cascadia (Green) | |||||
| Capital |
| ||||
| Largest city |
| ||||
| Official languages | English | ||||
| Ethnic groups | White, Native, Asian, Black, Pacific Islander | ||||
| Demonym | Cascadian | ||||
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic | ||||
| Tyler Barr | |||||
• Prime Minister of Cascadia |
Sophie Arab | ||||
• Chief Justice of Cascadia |
Michael Farnworth | ||||
| Legislature | Parliament of Cascadia | ||||
| Unicameral | |||||
| House of Commons | |||||
| Independence from Canada & United States | |||||
• Declared |
12th May 2013 | ||||
| Area | |||||
• Total |
4,865,211 km2 (1,878,468 sq mi) | ||||
| Population | |||||
• 2035 estimate |
36,252,667 | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2035 estimate | ||||
• Total |
$2,350,780,000 | ||||
• Per capita |
$64,000 (estimated) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2035 estimate | ||||
• Total |
2,141.651 billion | ||||
• Per capita |
$59,678 | ||||
| HDI (2025) |
0.949 very high · 3rd | ||||
| Currency | Cascadian Dollar | ||||
| Time zone | Pacific and Mountain (UTC-8/-7) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | ||||
| Calling code | +152 | ||||
| Internet TLD | .cas | ||||
|
Website www.cascadia.cas | |||||
The Commonwealth of Cascadia, more commonly known as Cascadia is a sovereign state consisting of 6 Provinces located primarily in western North America. One of the largest countries in North America, it is bordered by the Californian Republic and Deseret to the south, Canada, Wyoming and the Blackfoot Confederation to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Its capital city is Calgary whilst its largest city is Seattle. Cascadia has a single outside territory, located in Antarctica.
Cascadia, like many present-day North American countries, emerged out of a global crisis starting as a result of the early 21st century's global economic crisis. Its formation can primarily be attributed to a combination of economic necessity and political alienation of the west coast.
Early History[]
The area currently occupied by Cascadia was inhabited by countless indigenous tribes with populations numbering in the hundreds of thousands for millennia until European explorers arrived in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. Early exploration was undertaken by explorers from Spain but explorers from the United Kingdom, then known as Great Britain soon took over and established colonies in the area. The primary British colony in the area was known as "British Columbia", which became associated with the Dominion of Canada on the west coast in the 19th century following the completion of the Canadian Pacific (CP) Railway. Expansion of the United States in the later part of the 19th century led to what is known today as the "Oregon Boundary Dispute", in which disputed expansion plans led to joint administration of a region known then as the "Oregon Country". Later negotiations established a boundary along the 49th parallel and gave Britain's colony British Columbia control over Vancouver Island, where it remained until the establishment of Cascadia as an independent country in the early 21st century.
The idea of Cascadia as an economic cross-border region has been embraced by a wide diversity of civic leaders and organizations in the late 20th century and early 21st century. The "Main Street Cascadia" transportation corridor concept was formed by the former mayor of Seattle Paul Schell in 1991 and 1992. Schell later defended his cross-border efforts during the 1999 American Planning Association convention, saying "that Cascadia represents better than states, countries and cities the cultural and geographical realities of the corridor from Eugene to Vancouver, B.C." Schell also formed the Cascadia Mayors Council, bringing together mayors from cities along the corridor from Whistler, British Columbia, to Medford, Oregon. The council last met in May 2004. Other cross-border groups were set up in the 1990s, such as the Cascadia Economic Council and the Cascadia Corridor Commission. These groups were established to focus on transportation issues, and have not advocated secession or independence.
In the latter half of the first decade of the 21st century, the idea of including areas outside of the states of Washington, Oregon and the province of British Columbia came to light. There was talk of including Alberta specifically for the obvious economic advantages it would bring to a potential independent western state.
Modern History[]

Large rally in Vancouver, Columbia following the establishment of the Commonwealth of Cascadia
In June of 2009, following the global economic slowdown of the previous year, the Canadian province of Quebec held a referendum in an attempt to gain independence to both assert its own distinct identity and establish firmer control over its economy. The referendum, the third attempt of its kind was successful and Quebec became an independent republic. The states and provinces of both the United States and Canada were left in shock to see this happen, which led to several states becoming independent of the United States including Texas and Deseret. Northern California left California but remained with the Union for a short period as a state called Jefferson, which as a concept has origins in the mid-20th century. In the 2010s, increasing disputes between the west coast governments of Washington, Oregon, Jefferson, British Columbia, Alaska, Alberta, Montana and Idaho led to strengthened regionalism. Among the first to declare independence were British Columbia and Alberta following a ruling by a Canadian Supreme Court that a series of pipelines from resource-rich Alberta to ports at Kitimat, Prince Rupert and in the Lower Mainland were "unlawful to build". Alberta and British Columbia federated in May of 2013 to form the Pacific Federation, the second blow to what was an already-weakened Canadian federation. Seeing the actions of their neighbours to the north, Washington and Oregon bid within months to join the former Canadian provinces to form the nation-state now known as the Commonwealth of Cascadia. Jefferson and Alaska followed within a year, and by 2015, Cascadia's current borders were established through regional dialogue with locals. The pipelines from Alberta to the Pacific coast were built and a strong economic engine to drive the new country forward was up and running.
In the present day, large fields of oil have been discovered in the Beaufort Sea and municipalities along the northern coast including Prudhoe Bay, Utqiagvik/Nome and Inuvik have become regional boom towns as staging areas for getting the resource out of the ground.
Government and Politics[]

The Cascadian Federal Building, Calgary. The Cascadian Parliament meets at this former Canadian government office building.
Cascadia was established in its early forms as a decentralised Federal Parliamentary Republic, and it more or less retains this form of government to this day. The Parliament of Cascadia is a unicameral assembly consisting of representatives from a number of parties from across the country. The head of state, the President, is almost entirely a ceremonial role with some direct power for certain situations. This position is held for ten years at a term and can be renewed. The head of government, the Prime Minister is responsible for leading a cabinet, which makes decisions for the various ministries and divisions of the government. In addition, the Prime Minister is a sitting member of the Parliament, along with the members of the cabinet.
Much power is delegated to the governments of the various Provinces of Cascadia, which are responsible for most items that affect the daily lives of citizens, such as education, healthcare and infrastructure. The federal government is primarily responsible for dealing with items on the global stage, such as trade, border security, defense and international relations, among other things. The Cascadian Parliament has 150 seats from throughout the country, and meets in the capital city of Calgary in the former Harry Hays building. The founding government stated that Calgary was chosen as the capital city for Cascadia for a number of reasons, most notably to pay tribute to the contributions of Alberta's energy sector to the national economy, but primarily to not have a capital exposed to potential aggression from across the Pacific.
Chancellor[]
The President of Cascadia is the head of state position of the Government of Cascadia. However, the role of the Chancellor is generally considered to be ceremonial and the broad powers of the Chancellery are meant to be used infrequently. All legislation passed by the Parliament must be signed off by the Chancellor. Other powers, such as arbitration on controversial legislation, directing the courts to review potentially unconstitutional legislation and making recommendations to the government on legislation that should be put forward are among those that are held by the Chancellor. The Chancellor also holds the position of Chancellor until death or retirement, at which time the Parliament of Cascadia must elect a new Chancellor.
Because of the figurehead role with a potentially unlimited term length, many scholars consider the Cascadian Chancellor to be more of a monarch with limited power than a head of state with a parliamentary system of government. The role has been compared to that of the more recent monarchs of the United Kingdom. It is argued that Cascadia is a de facto constitutional monarchy.
Prime Minister[]
The Prime Minister of Cascadia is the head of government position of the Government of Cascadia. The majority of actual decision-making power lies in the position of the Prime Minister, including the signing in of legislation, the direction of the military, and speaking on behalf of the government (both domestically and internationally), among a slew of other things.
The Prime Minister is elected as the leader of the federal political party which receives the most seats in Parliament. The role is held for four years a term with a limit set for individuals holding the position for no more than two consecutive terms. In Parliament, the Prime Minister acts as both the leader of their respective political party and the Member of Parliament for their constituency. It is up to the party's administration and the Parliament as a whole to ensure that the Prime Minister is acting in the best interests of both their constituents and the citizens of the country as a whole while in that particular position.
Parliament[]
The Parliament of Cascadia is a unicameral house consisting of a total of 150 Members of Parliament (MP for short). Cascadia is divided up into 150 constituencies, and MPs are elected 1 per constituency. MPs run under a political party but are responsible directly to their constituents. Legislation is in place to allow constituents to put forward a petition to recall a serving MP that is performing unsatisfactorily. MPs hold their offices in 4-year terms and can be re-elected multiple times.

Government of Cascadia Wordmark
Geography[]
Detailed Map[]
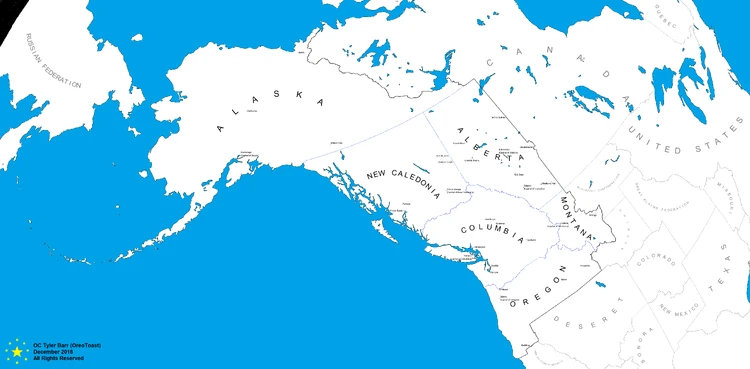
Map of Cascadia with cities of regional importance highlighted.
Cascadia is organized as a federation of six constitutionally equal provinces.
Alaska[]

Flag of Alaska
Alaska is the largest and northernmost province in Cascadia. It consists of the former US State of Alaska (for which it is named), the former Canadian territory of the Yukon and the Northwest Territory west of the Mackenzie River. Its geography is primarily tundra, mountains and forest. With recent global warming trends, small tracts of land have become suitable for agriculture in Alaska. Alaska has vast reserves of primarily ore resources, and as of recently, vast offshore oil reserves.
Most of northern Alaska's wilderness is protected as a Parks Cascadia National Park. The capital city of Alaska is Anchorage.
Alberta[]

Flag of Alberta
Alberta is Cascadia's second largest province and consists of the former Canadian Province of Alberta, along with small western parts of the Canadian Province of Saskatchewan, mostly surrounding the city of Lloydminster. It also plays host to the capital city of Cascadia. Alberta's geography is incredibly diverse, ranging from vast boreal forests in the north to some of the northernmost portions of the North American Great Plains in the south, to the majestic Rocky Mountains in the west. Alberta, with its vast reserves of effectively every type of resource and industry, including natural gas, oil sands, coal and others such as tourism, technology and agriculture leaves it to function as the economic engine of Cascadia.
Columbia[]

Flag of Columbia
Columbia is Cascadia's most populous province, with two major cities -Vancouver and Seattle- existing effectively right next door to each other, forming an almost contiguous built-up area. Columbia consists of the southern portion of the former Canadian province of British Columbia (from which the province's name is derived), along with the former US State of Washington and portions of northern Idaho. Much of Columbia's geography consists of mountainous and hilly forested areas, though some areas are suitable for agricultural development, such as the Fraser River's delta, where the Vancouver metropolitan area is located. Columbia plays host to a thriving tourism industry, especially along its coast and on lakes in its interior, such as the Okanogan. There is also a decently sized resource sector in the northern and southern parts of the province.
Montana[]

Flag of Montana
Montana is Cascadia's smallest province, both by area and population. It primarily consists of the western half of the former US state of Montana, but it also has portions of the former US State of Wyoming. It is geographically divided, with the Rocky Mountains in the west and the Great Plains in the east. Montana has strong mining and agriculture sectors, which has led to it being known as the "second breadbasket", concerning Alberta.
New Caledonia[]

Flag of New Caledonia
New Caledonia is among the larger of Cascadia's provinces by land area, but it ranks low on the population chart, having only a handful of cities over 10,000 people, and only one over 100,000. New Caledonia consists of the northern portion of the former Canadian province of British Columbia. Its geography is split primarily between vast hilly boreal forests and mountains, both in the east and west. Some isolated areas, primarily in river valleys are suitable for agricultural development, however. New Caledonia has a strong tourism sector, having large swaths of untouched wilderness which appeal to trekkers from around the world. It also possesses a vast resource economy, particularly in forestry and natural gas.
Oregon[]

Flag of Oregon
Oregon has a vast geography, extending from the coast of the Pacific Ocean to over 1000km inland in the western portion of the former US State of Wyoming. It consists of the former US States of Oregon, the southern portion of Idaho and the western portion of Wyoming. Oregon's geography is varied, having lush forests along its coast, a rain shadow steppe and numerous mountain ranges. This varied geography has enabled Oregon to have a varied economy, including strong tourism, particularly on the coasts and in the mountains, and a strong agriculture sector (particularly ranching).
Climate Map[]
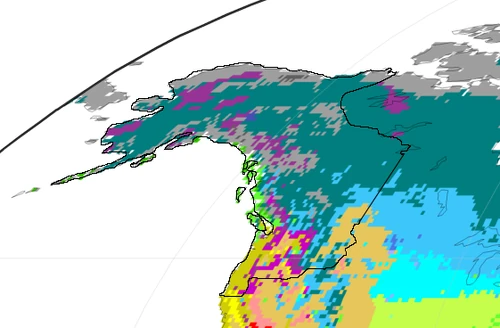
Cascadia has a wildly varied climate, ranging from dry, desert-like arid areas to plains to vast boreal forests and lush coastal rainforests. The varied climate of Cascadia has provided immense benefits to the domestic economy, both in the various resource sectors and tourism.
Under the Köppen climate classification system, the majority of Cascadia's landmass falls under various forms of what is classified as a 'subarctic climate', or Dfc, with other significantly sized areas falling under what the classification system classifies as hot and cold semi-arid climate zones. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are A (tropical), B (dry), C (temperate), D (continental), and E (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the E group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, Af indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the A group, indicated by the third letter for climates in B, C, and D, and the second letter for climates in E. For example, Cfb indicates an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending b. Climates are classified based on specific criteria unique to each climate type.
Economy[]

Suncor Corporation's upgrader near Wood Buffalo, Alberta
Thanks to the vastness of Cascadia and the sheer variety of natural resources the land provides, Cascadia possesses a strong, diversified economy.
The strongest sector of Cascadia's economy is currently energy and natural resources. The strongest areas of these economic sectors are currently Alberta and New Caledonia, with the most notable center of energy development continuing to be located at the Wood Buffalo (formerly Fort McMurray) Oil Sands. This sector is second to a rapidly expanding technology sector, and third to a sector that continues to prosper: commerce. Many international companies have moved their headquarters to Cascadian cities, including but not limited to Amazon and its e-commerce operations, and Google and their increasingly advanced technology operations.
Cascadian law allows for the creation of what is known as "Special Economic Zones", in which exceptions to particular laws such as environmental laws and labour laws can be made on a case-by-case basis. One major example of this is the Wood Buffalo Oil Sands, where a zone has been created to allow for the broader development of oil sands in the region. All exceptions made are reviewed by a government committee. Most exceptions made are for environmental laws, primarily to protect workers.
Currency[]
Cascadia has its currency and maintains its banknotes. The value of Cascadia's banknotes is tied to the gold standard. In Cascadia's earlier days, US and Canadian currencies were still accepted on both sides of the former border while the new currency was implemented.
Culture and National Identity[]
Unlike many states, Cascadia's identity is not primarily based on culture, but rather its geography. The origins of the Cascadian polity stemmed originally from an increasing amount of regionalism and a feeling of alienation from federal governments on the east coast of the continent. Many Cascadians find they can identify more with the new Cascadian state along the Pacific coast than they were previously able to identify with the Canadian and American states before independence.
Cascadia's culture is largely a regional thing, with attitudes and practices varying somewhat depending on location. For example, attitudes about industry vary between major urban centres and boom towns, and even areas inside of national parks.
Sports Leagues[]
North American Hockey League[]
The successor to the former National Hockey League (NHL), the North American Hockey League (NAHL) was created in 2010 amongst the newly formed states of North America following the geopolitical shakeups following the economic crisis of 2008. Cascadia currently has a total of four ice hockey teams in the NAHL and is in the progress of expanding to five.
| Team Name | Logo |
|---|---|
| Edmonton Oilers |  |
| Calgary Flames | |
| Vancouver Orcas | |
| Seattle Steelheads |  |
Cascadian Football League[]
Otherwise known as the Cascadian Gridiron League, the Cascadian Football League (CFL) is the Cascadian successor to the Canadian Football League (also CFL) and the US National Football League (NFL). Like its ice hockey counterpart, it was created in the wake of the 2008 economic crisis. The CFL has a number of teams from all across the country.
| Team | Logo/Helmet |
|---|---|
| Edmonton Eskimos | |
| Calgary Stampeders | |
| Vancouver Lions | |
| Seattle Seahawks | |
| Portland Breakers |  |
| Anchorage Seawolves |
Armed Forces[]
Cascadian Armed Forces Roundel
Cascadia's armed forces, centralized under the command of what is known as the Cascadian Armed Forces, consist of the Cascadian Army, the Cascadian Air Force and the Cascadian Navy. Cascadia possesses a well-trained armed force totalling around 175,500 active members, with 50,000 reserve members. This number does not include various other armed non-military forces, which include the Cascadian Coast Guard and the Cascadian Federal Police Service.
Army[]
The Cascadian Army is the largest force that falls under the command of the Cascadian Armed Forces, consisting of around 100,000 members. The Cascadian Army commands sub-branches of various infantry (ground troops), armoured cavalry (APCs, tanks) and artillery (howitzer guns, mortars).
The majority of the army division of the armed forces are infantry troops, second to cavalry and artillery. Several enlisted personnel also serve as mechanics and as Military Police officers.
The Army is distinct from the other two service branches in that the majority of its personnel are active members rather than support members; most members could potentially find themselves at the front lines in the event of a confrontation.
Air Force[]

Military Policeman guards an F-22 Raptor Jet, Cascadia's standard fighter jet.
The Cascadian Air Force is the second largest force under the command of the Cascadian Armed Forces, numbering at around 40,000 active members. The Cascadian Air Force consists of a largely varied complement of aircraft, some acquisitions from both the American and Canadian Air Forces during the move into independence, and some acquisitions through purchase by the military. There are around 600 active aircraft in service to the Cascadian Air Force, ranging from fighter jets to helicopters to heavy-lift jet aircraft. Similar to the Army, the roles of the Air Force's personnel vary greatly: only some members are actual aircraft pilots, and others are aircrew who serve to support pilots directly, such as navigations officers for C-17 heavy-lift jets and launch crew for fighter jets. Other personnel may be mechanics or other support crew. The Air Force also has its own, separate Military Police force which serves to both protect Air Force assets and maintain discipline within the branch.
[]

A refitted Arleigh-Burke Class Destroyer off the coast of Columbia.

Emblem of the Cascadian Navy
The Cascadian Navy is the smallest force under the command of the Cascadian Armed Forces. The navy's personnel numbers are around 35,500 active members. The number of vessels currently in service to the Cascadian Navy number around 75 vessels of all types, ranging from patrol craft to destroyers to aircraft carriers. The majority of Cascadia's naval assets were requisitioned during the independence process, though some were acquired through means of purchase. The majority of Cascadia's naval complement consists of older vessels, however, significant investment has been made in refitting their systems top to bottom, particularly in communications, weaponry and engines.
Cascadia makes a point of maintaining a navy with a significant level of strength to assert itself in the continually melting arctic ocean, where vast caches of oil and natural gas have been discovered offshore.

Ships of the Cascadian Navy
Acknowledgements[]
Acknowledgements[]
Wikipedia for just being great!
User:Dog of War for inspiring me with Rainier and for creating the infobox I used as a template for this!
DeviantArt user Azzolubianco for the Greater Coat of Arms and motto!
DeviantArt user Kristberinn for the Armed Forces Roundel
AlternateHistory user MovingtargeT for the Armed Forces Uniforms
This paper for providing some plausibility basis for this concept
This article for providing a look at what the west might do following Quebec secession






















